Double Star Observation SAO118981(=XZ17514,=ZC1692) in Apr.28 2007
Kazuhisa Miyashita
Apr.29 2007
reviced May 5. 2007
1.Abstract
Masayuki Ishida (Moriyama ,Shiga) and Tomohisa Ohno (Kurashiki, Okayama) respectively sent me the Limovie's CSV file of observation of a double-star SAO118981. (Ishida had analyzed his observation himself. Ohno's observation was analyzed by Kunio Kenmotsu.) And I also observed same event at Ikeda-Town, Nagano Pref.. I analyzed these observations using Limovie. The result of astrometry and photometry are as follows.
|
Table 1. Result of analysis |
||
|
|
Observation |
Catalog |
|
Separation (arcsec) |
0.68 +/- 0.10 |
0.8 |
|
Position Angle (degree) |
127 +/- 10 |
130 |
|
If the magnitude of the pair is 6.92 then .. |
||
|
First star(mag) |
7.00 +/- 0.03 |
6.9 |
|
Second star(mag) |
9.79 +/- 0.42 |
9.9 |
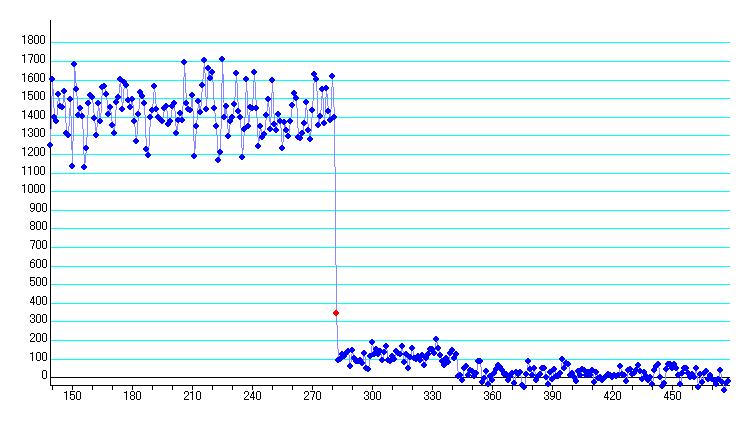
2. Limovie plot (overview luminous change)

Figure 1. Moriyama, Shiga
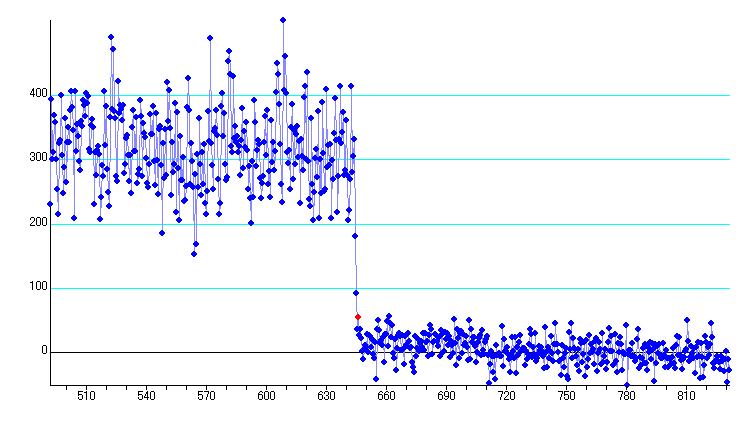
Figure 2. Ikeda, Nagano
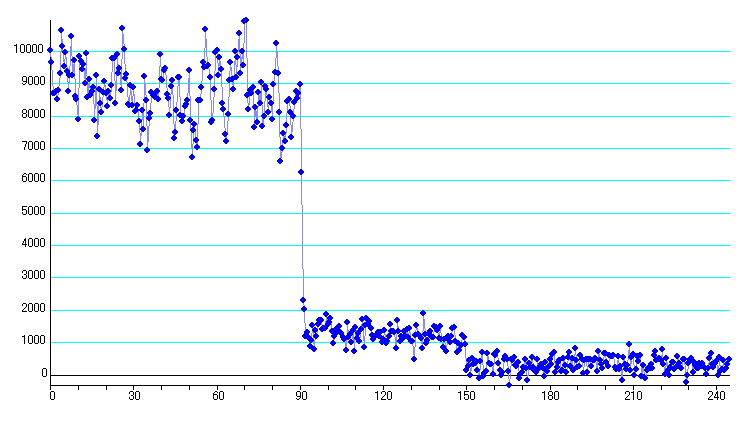
Figure 3. Kurashiki, Okayama
Analyzed by Kunio Kenmotsu
3. Predictions and calculating parameters for analysis
3-1 Prediction
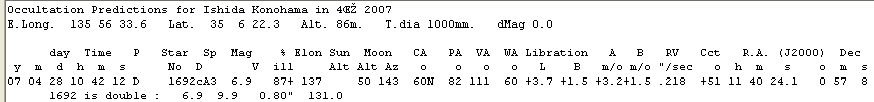
Table 2 Prediction derived from LOW
for Konohama, Shiga
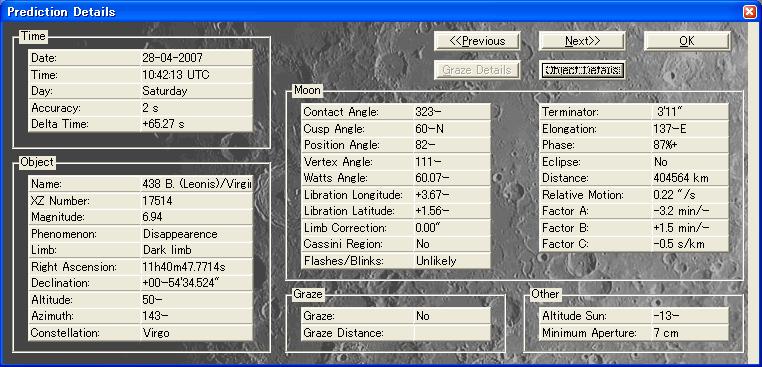
For Ikeda, Nagano
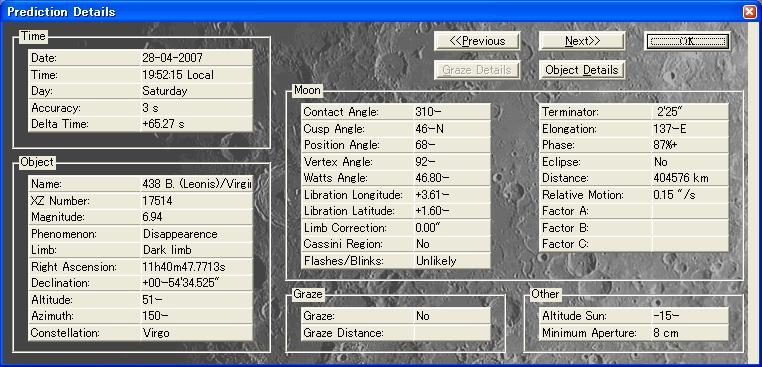
for Kurashiki, Okayama
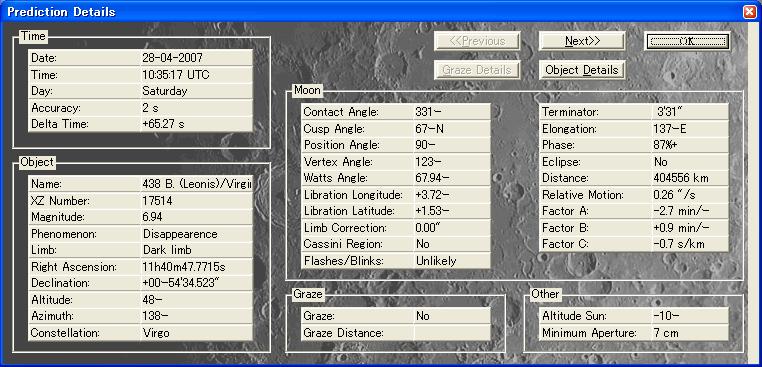
Table 3 Prediction derived from Win OCCULT.
For Moriyama, Shiga
For Ikeda, Nagano

For Kurashiki, Okayama

3-2 Caluclate Linar velocity
|
Calculation of Lunar Velocity |
||||||||
|
Date |
2007/04/28 |
Va |
|
|
Va : Velocity as angle (“/sec) |
|||
|
Event |
CCT |
51.0 |
|
CCT:Contact Angle (from OCCULT) |
||||
|
SAO118981 |
RV |
0.218 |
|
RV : Radial Velocity (from OCCULT) |
||||
|
Station |
Ds |
404576 |
|
Ds : Moon distance (from LOW) |
||||
|
Moriyama, Shiga |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
d |
m |
s |
|
Then, moon velocity V (m/sec) is calculated as follows. |
|||
|
Long. |
135 |
56 |
33.6 |
|
RV = cos(CCT)* Va |
|||
|
Lat. |
35 |
6 |
22.3 |
|
Va = RV / abs(cos(CCT)) |
|||
|
Hight |
86 |
m |
= |
0.3464 |
|
(arcsec/sec) |
||
|
Observer |
V = Ds*π*Va/(180*3600)*1000 |
|||||||
|
Masayuki Ishida |
= |
679 |
|
(m/sec) |
||||
|
Calculation of Lunar Velocity |
||||||||
|
Date |
2007/04/28 |
Va |
|
|
Va : Velocity as angle (“/sec) |
|||
|
Event |
CCT |
42.0 |
|
CCT:Contact Angle (from OCCULT) |
||||
|
SAO118981 |
RV |
0.260 |
|
RV : Radial Velocity (from OCCULT) |
||||
|
Station |
Ds |
404556 |
|
Ds : Moon distance (from LOW) |
||||
|
Ikeda, Nagano |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
d |
m |
s |
|
Then, moon velocity V (m/sec) is calculated as follows. |
|||
|
Long. |
137 |
54 |
4.2 |
|
RV = cos(CCT)* Va |
|||
|
Lat. |
36 |
22 |
8.1 |
|
Va = RV / abs(cos(CCT)) |
|||
|
Hight |
600 |
m |
= |
0.3499 |
|
(arcsec/sec) |
||
|
Observer |
V = Ds*π*Va/(180*3600)*1000 |
|||||||
|
Kazuhisa Miyashita |
= |
686 |
|
(m/sec) |
||||
|
Calculation of Lunar Velocity |
||||||||
|
Date |
2007/04/28 |
Va |
|
|
Va : Velocity as angle (“/sec) |
|||
|
Event |
CCT |
42.0 |
|
CCT:Contact Angle (from OCCULT) |
||||
|
SAO118981 |
RV |
0.260 |
|
RV : Radial Velocity (from OCCULT) |
||||
|
Station |
Ds |
404556 |
|
Ds : Moon distance (from LOW) |
||||
|
Kurashiki, Okayama |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
d |
m |
s |
|
Then, moon velocity V (m/sec) is calculated as follows. |
|||
|
Long. |
133 |
47 |
42.42 |
|
RV = cos(CCT)* Va |
|||
|
Lat. |
34 |
34 |
49.56 |
|
Va = RV / abs(cos(CCT)) |
|||
|
Hight |
66 |
m |
= |
0.3499 |
|
(arcsec/sec) |
||
|
Observer |
V = Ds*π*Va/(180*3600)*1000 |
|||||||
|
Tomohisa Ohno |
= |
686 |
|
(m/sec) |
||||
4. Diffraction Analysis
4-1. Moriyama, Shiga.
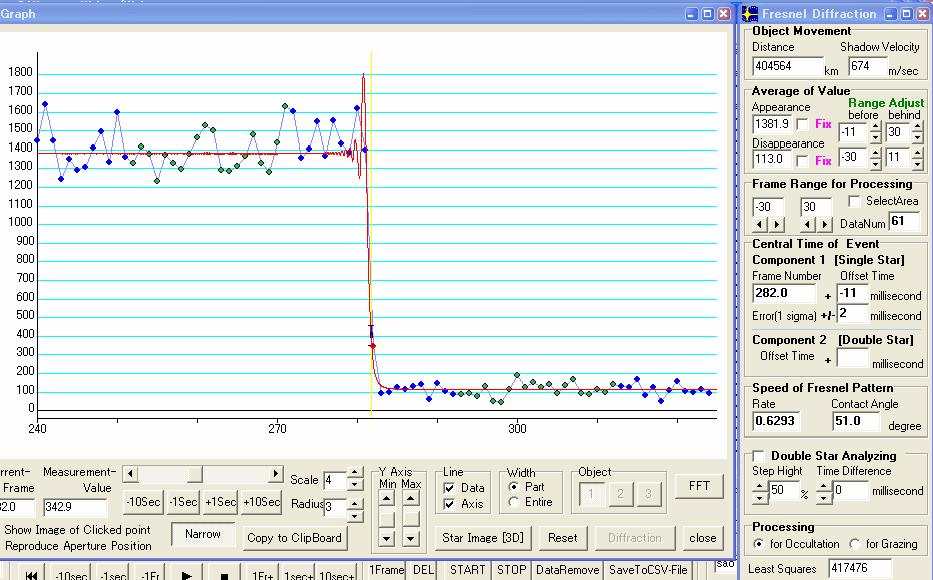
Figure 4.Disappearance of first star
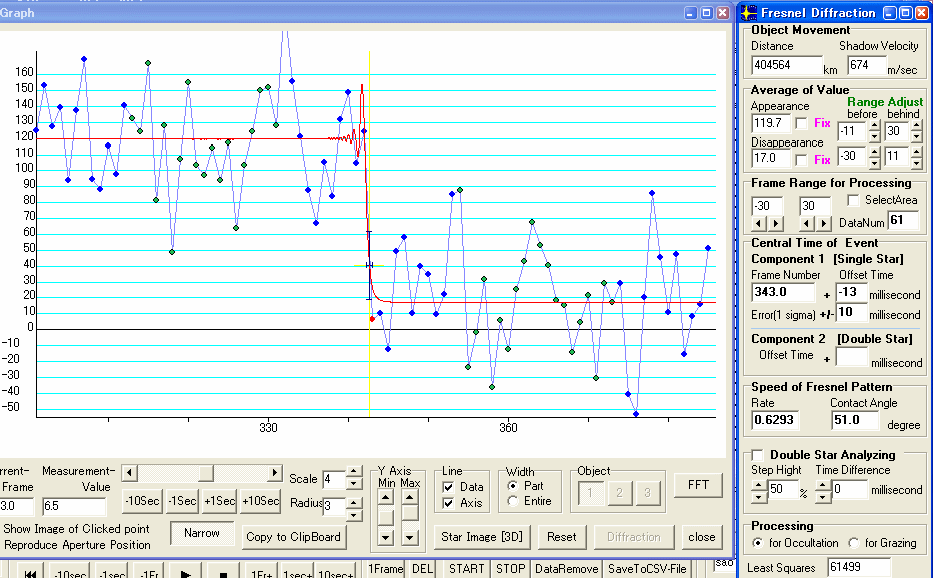
Figure 5. Disappearance of second star
This measurement is frame by frame. So the event time is calculate using the time of frame centre which is the later time displayed at the Field Show mode,.
First star : No.282 Frame -11 millisecond +/- 2 millisecond
Time of TIVi (centre of frame) is No.282=10h42m12.23s then event time is 10h42m12.22s
Hence, the event time is 10h52m10.190sSecond star : No.343 Frame -13 millisecond +/- 10 millisecond
Second Star : No.343 Frame -13 millisecond +/- 10 millisecond
Time of TIVi (centre of frame) is No.343=10h42m14.27s then event time is 10h42m14.26s
Time Difference = 61 Frames – 2 millisecond = 61 / 29.97 – 0.002 second = 2.035 – 0.002 = 2.033 second
4-2. Ikeda, Nagano
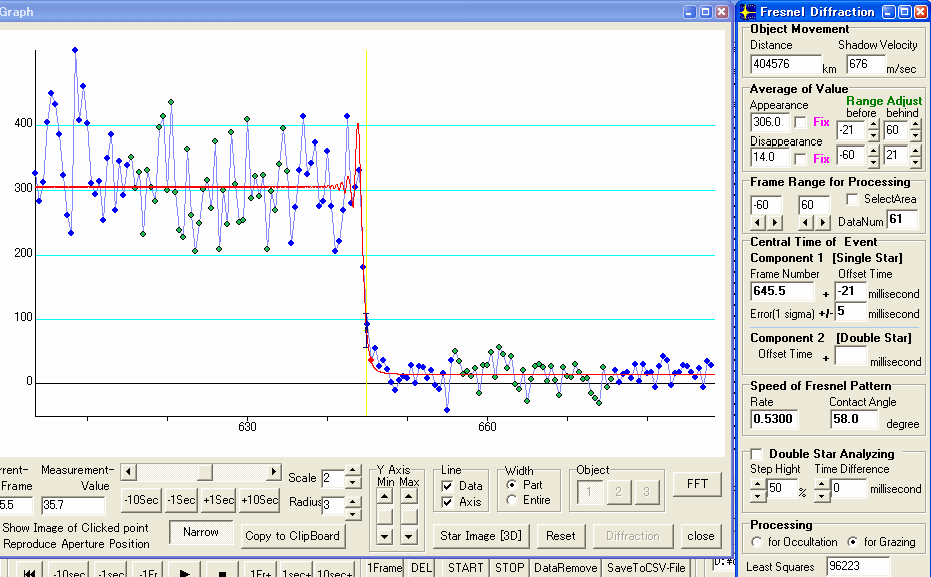
Figure 6. Disappearance of first star
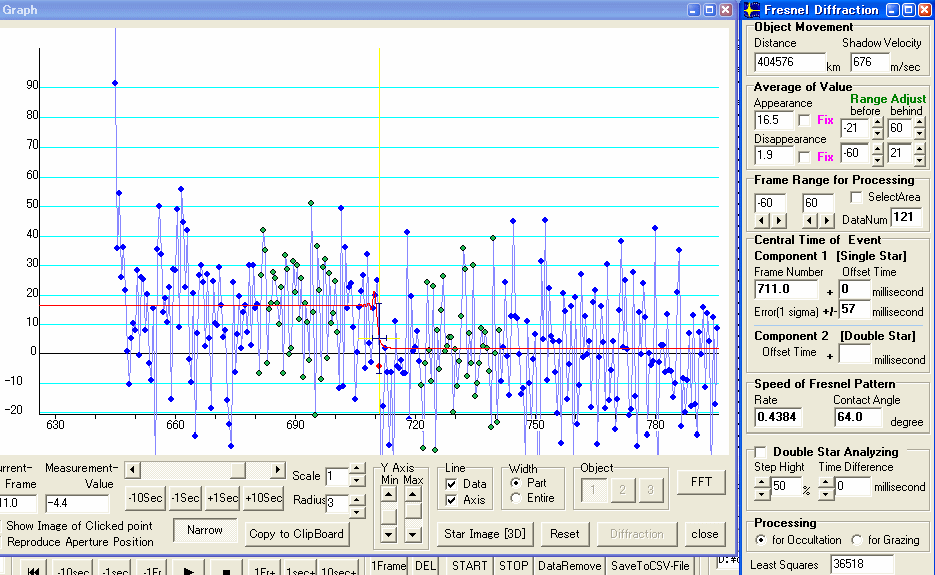
Fugure 7. Disppearance of second star
This measurement is field by field. So the event time is calculate using the time of field. The field central time is necessary to calculate using displayed times.
First
omponent : No.645.5 Frame -21 millisecond +/- 5 millisecond
Time
of KIWI-OSD are .. at field start :10h52m10.194s, at field end :
10h52m10.227s. Then centre of field is 10h52m10.211s .
Hence, the event time is 10h52m10.190s
Second component : No.711.0 Frame +0 millisecond +/- 57 millisecond
Time of KIWI-OSD are .. at field start :10h52m12.363s, at field end : 10h52m12.396s. Then centre of field is 10h52m12.380s .
Hence, the event time is 10h52m12.380s
Time Difference = 2.190 second
4-3. Kurashiki, Okayama
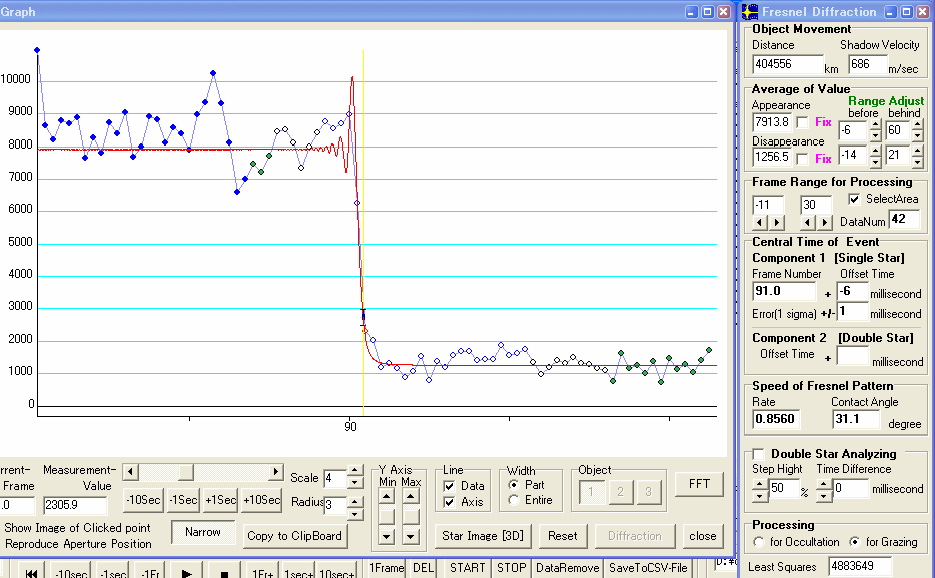
Figure 8. Disappearance of first star
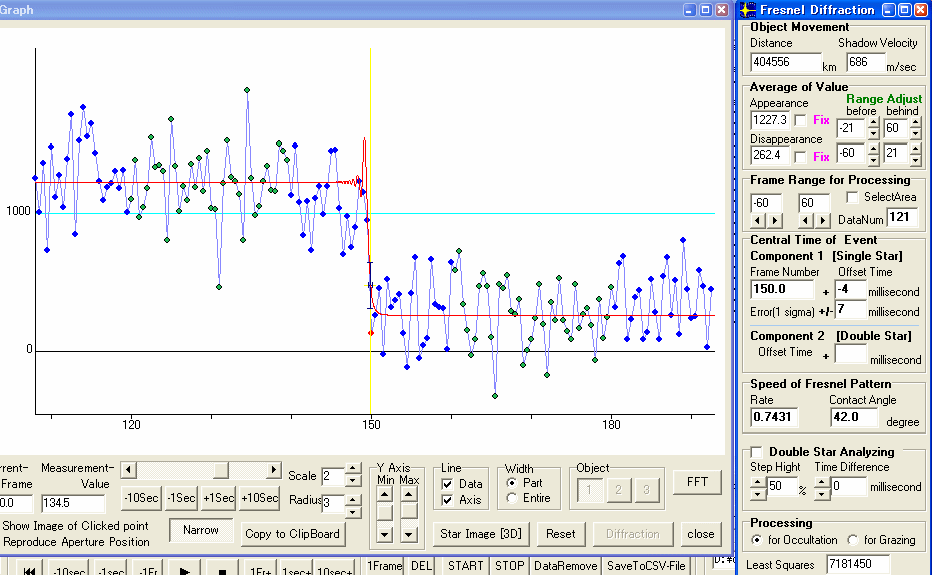
Figure 9. Disappearance of second star
|
|
Frame begining |
Field centre |
Field end / Frame centre |
|
No.91 |
10h 35m 16.39s |
10h 35m 16.40s |
10h 35m 16.41s |
|
No.150 |
10h 35m 18.36s |
10h 35m 18.37s |
10h 35m 18.38s |
First star : No.91.0 Field -6 millisecond +/- 1 millisecond
then, the event central time is 10h 35m 16.40s – 6millisecond = 10h 35m 16.39s
Second star : No.150.0 Field - 4 millisecond +/- 7 millisecond
then, the event central time is 10h 35m 18.37s – 4millisecond = 10h 35m 18.37s
Time Difference = 59 Frames + 2 millisecond = 69 / 29.97 + 0.002 second = 1.971 second
5. Astrometry
|
Figure 10. Position of component and lunar limb |
Case of b2>b1 From Fig、6 b1=a*sin A --------------(1) b2=a*sin(A+P1-P2) --------(2) C=P1-P2 b2=a*sin(A+C) =a*(sinA*cosC+cosA*sinC) =a*sinA*cosC+a*cosA*sinC --(3) From (1) a = b1/sinA --------------(4) put into (3) b2 = (b1/sinA)*sinA*cosC +(b1/sinA)*cosA*sinC b2 = b1*cosC+b1*(1/tanA)*sinC b2 = b1*cosC+b1*sinC/tanA b2 = b1(cosC+sinC/tanA) b2/b1 = cosC + sinC/tanA b2/b1 - cosC = sinC/tanA (b2/b1 - cosC)/sinC = 1/tanA tanA = sinC/(b2/b1 - cosC) --(5) put A into (4) and obtain separation a. Hence Position Angle P is P=90-(p1+A) ----------------(6)
In the case of b1>b2 then a=b2/sinA ----------------(4) tanA = sinC/(b1/b2 - cosC) –-(5) P=90+p2-A ----------------(6) |
5-1 Kurashiki-Moriyama
|
Station |
1 |
2 |
|
|
Kurashiki |
Moriyama |
|
|
|
PA around Moon(Px) |
90 |
82 |
Should be P1>P2 |
|
Radial Velocity |
0.260 |
0.218 |
(arcsec/sec) |
|
Time Difference |
1.971 |
2.190 |
(sec) |
|
Radial Distance(b) |
0.599 |
0.477 |
(arcsec) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
C=P1-P2 |
8 |
degree |
|
|
This case is... |
b1>=b2 |
then |
|
|
A |
59.15 |
degree |
|
|
Position Angle (P) |
113 |
degree |
|
|
Separation (a) |
0.56 |
arcsec |
|
5-2 Kurashiki-Ikeda
|
Station |
1 |
2 |
|
|
Kurashiki |
Ikeda |
|
|
|
PA around Moon(Px) |
90 |
68 |
Should be P1>P2 |
|
Radial Velocity |
0.260 |
0.151 |
(arcsec/sec) |
|
Time Difference |
1.971 |
2.033 |
(sec) |
|
Radial Distance(b) |
0.599 |
0.307 |
(arcsec) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
C=P1-P2 |
22 |
degree |
|
|
This case is... |
b1>=b2 |
then |
|
|
A |
26.78 |
degree |
|
|
Position Angle (P) |
131 |
degree |
|
|
Separation (a) |
0.68 |
arcsec |
|
5-3 Moriyama-Ikeda
|
Station |
1 |
2 |
|
|
Moriyama |
Ikeda |
|
|
|
PA around Moon(Px) |
82 |
68 |
Should be P1>P2 |
|
Radial Velocity |
0.218 |
0.151 |
(arcsec/sec) |
|
Time Difference |
2.190 |
2.033 |
(sec) |
|
Radial Distance(b) |
0.477 |
0.307 |
(arcsec) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
C=P1-P2 |
14 |
degree |
|
|
This case is... |
b1>=b2 |
then |
|
|
A |
22.47 |
degree |
|
|
Position Angle (P) |
136 |
degree |
|
|
Separation (a) |
0.80 |
arcsec |
|
5-4 Result
|
|
average |
|
rms |
|
|
Position Angle (P) |
127 |
+/- |
10 |
degree |
|
Separation (a) |
0.68 |
+/- |
0.10 |
Arcsec |
These values are well corresponding to the description of catalog .
6. Magnitude of components
|
Calculation of the magnitude of components |
||||
|
Object |
SAO |
XZ |
ZC |
|
|
|
118981 |
17514 |
1692 |
|
|
Station / Observer |
Moriyama, Shiga |
Masayuki Isida |
||
|
|
Measure1 |
Measure2 |
Average |
|
|
Lunimous of pair |
1381 |
|
1381 |
unit |
|
Step |
119.7 |
113 |
116.35 |
unit |
|
Background |
17 |
|
17 |
unit |
|
Step-Background is formed by .. |
Second Component |
|||
|
Luminous of first star |
|
|
1264.65 |
unit |
|
Luminous of second star |
|
|
99.35 |
unit |
|
Lunious of pair |
|
|
1364 |
unit |
|
from the canalog the pair is |
|
|
6.92 |
Mag. |
|
from the formula m1-m2 = 2.5 log(b2-b1) |
||||
|
The difference in magnitude of the two star is .. |
2.76 |
Mag. |
||
|
if the magnitude of the pair is |
6.92 |
then the magnitude of first star is .. |
||
|
from the formula m1 = 2.5 log(bp-b2) +mp |
||||
|
Magnitude |
First component |
7.00 |
Mag. |
|
|
|
Second component |
9.76 |
Mag. |
|
|
Calculation of the magnitude of components |
||||
|
Object |
SAO |
XZ |
ZC |
|
|
|
118981 |
17514 |
1692 |
|
|
Station / Observer |
Kurashiki, Okayama |
Tomohisa Ohono |
||
|
|
Measure1 |
Measure2 |
Average |
|
|
Lunimous of pair |
8757.8 |
|
8757.8 |
unit |
|
Step |
1269 |
|
1269 |
unit |
|
Background |
319.3 |
|
319.3 |
unit |
|
Step-Background is formed by .. |
Second Component |
|||
|
Luminous of first star |
|
|
7488.8 |
unit |
|
Luminous of second star |
|
|
949.7 |
unit |
|
Lunious of pair |
|
|
8438.5 |
unit |
|
from the canalog the pair is |
|
|
6.92 |
Mag. |
|
from the formula m1-m2 = 2.5 log(b2-b1) |
||||
|
The difference in magnitude of the two star is .. |
2.24 |
Mag. |
||
|
if the magnitude of the pair is |
6.92 |
then the magnitude of first star is .. |
||
|
from the formula m1 = 2.5 log(bp-b2) +mp |
||||
|
Magnitude |
First component |
7.05 |
Mag. |
|
|
|
Second component |
9.29 |
Mag. |
|
|
Calculation of the magnitude of components |
||||
|
Object |
SAO |
XZ |
ZC |
|
|
|
118981 |
17514 |
1692 |
|
|
Station / Observer |
Moriyama, Shiga |
Masayuki Isida |
||
|
|
Measure1 |
Measure2 |
Average |
|
|
Lunimous of pair |
306 |
|
306 |
unit |
|
Step |
14 |
16.5 |
15.25 |
unit |
|
Background |
1.9 |
|
1.9 |
unit |
|
Step-Background is formed by .. |
Second Component |
|||
|
Luminous of first star |
|
|
290.75 |
unit |
|
Luminous of second star |
|
|
13.35 |
unit |
|
Lunious of pair |
|
|
304.1 |
unit |
|
from the canalog the pair is |
|
|
6.92 |
Mag. |
|
from the formula m1-m2 = 2.5 log(b2-b1) |
||||
|
The difference in magnitude of the two star is .. |
3.35 |
Mag. |
||
|
if the magnitude of the pair is |
6.92 |
then the magnitude of first star is .. |
||
|
from the formula m1 = 2.5 log(bp-b2) +mp |
||||
|
Magnitude |
First component |
6.97 |
Mag. |
|
|
|
Second component |
10.31 |
Mag. |
|
Three values are obtained. It is considered that the three observations are suitable for meazuring the luminous intensity, because the star profiles recorded in the video tape aren't saturated. Three values are calculatad, and results are obtained as average and rms. The magnitude of components are :
First component : 7.01 +/- 0.03 Mag.
Second component : 9.79 +/-0.42 Mag.
It is well corresponding to the catalog description.